HIGHLIGHTS
- Bullwhip effect is the phenomenon of distortion in demand when going upstream or downstream the supply chain.
- The root cause behind that is the asymmetric information between entities in the supply chain. That can be depicted in many aspects.
- Coordination, stable price policy, supply chain optimization, etc. are the key solutions to tackle this effect.
FULL ARTICLE
1. What is the Bullwhip Effect?
The Bullwhip Effect is a phenomenon in which information about demand for products is distorted as it upstream or downstream the supply chain, leading to excess inventory, pricing fluctuation, and deviation in the market demand.
For example:

A retailer sells 10 ice creams per day on average. In the peak summer, sales increased to 30 pcs/day. Thus, the retailer decided to order 40 pcs/day from wholesalers (10 spares).
Wholesalers also have a similar backup mentality, so instead of ordering 40 units, they ordered 60 units.
Similarly, the manufacturer decides to produce 80 units/day. Obviously, through many entities, the actual needs have been magnified many times, creating a wave of virtual demand and waste. This phenomenon is known as the Bullwhip Effect. It was first discovered by Dr. Ray Forrester in 1961.
2. Impact of the Bullwhip Effect on the Supply Chain
The Bullwhip effect causes significant impacts on the performance of supply chains and businesses
- Rising costs: Bullwhip effect is the cause of inventory excess, which directly increases the holding and handling costs. In addition, maintaining the product quality for a long time in warehouses is also another challenge for enterprises.
- Stagnating the flow of materials: excessive production puts pressure on the distribution system because almost all demands are met. That leads to the phenomenon of stagnation in product and investment flows.
- Losing competitive advantages: this origins from costs increasing when Bullwhip occurs. Thus, enterprises have to raise the price to set off the loss which perhaps causes the loss of competitive advantage.
3. Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
The core reason behind demand distortion is attributed to asymmetric information between the entities of the supply chain. Their manifestations can be depicted as follows:
- The way to update information to forecast demand
Each entity in the supply chain often conducts demand forecasts, which serves as the basis for developing operational plans. Forecasts are usually based on historical demand data from direct customers.
For example, based on the data of orders from the retailer, the wholesaler will make demand forecasts for the future. The very nature of this shows the lack of multi-dimensionality when using only direct customer data without a comprehensive view of the market.
This is one of the key factors causing the Bullwhip effect.
- Order batch
Many businesses consolidate orders to gain economies of scale (the EOQ model is the backbone). That may cause the misunderstanding that actual demands are increasing.
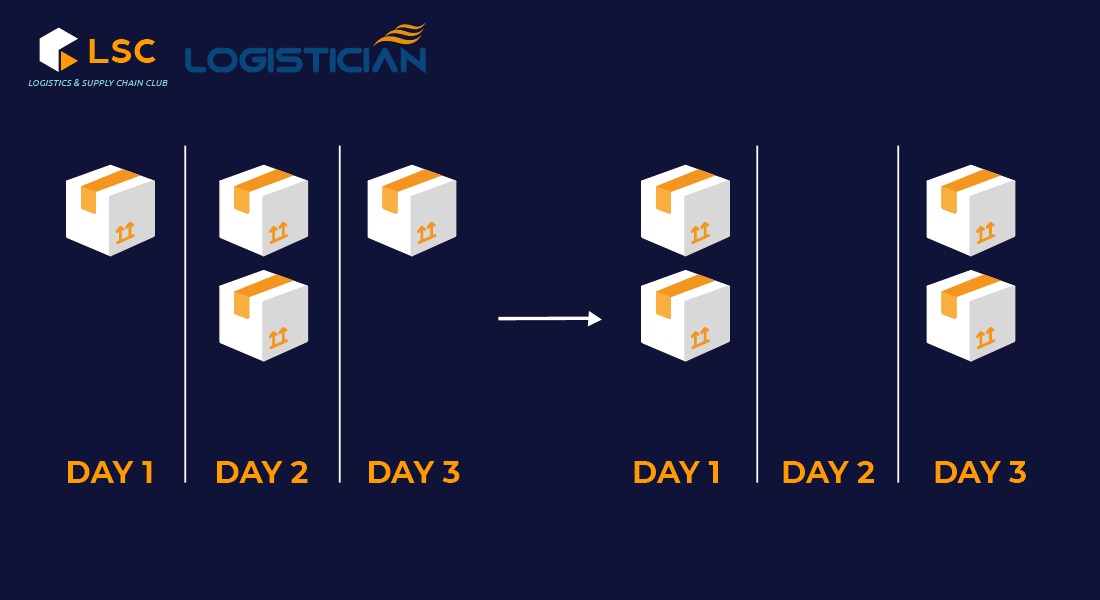
Since 2004, Holland and Sodhi have been working on a two-tier supply chain model of retailers and manufacturers in which retailer must order at integer multiples of lot size (e.g. for bulk quantities with the order is 50 units, lot size must be 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, or 50).
They found that the magnitude of bullwhip effect is in direct proportion to the size of order.
- Price volatility
Promotions like discounts, rebates, etc. are used to stimulate sales, and they lead to price fluctuations. This stimulates customers to buy more, in larger quantities but makes the perception of actual demand somewhat misleading. So the Bullwhip effect appears again.

- The game reacting to shortages
When the demand exceeds the supply, the supplier will allocate the proportion according to the ordered quantity. If supply can meet only 50% of demand, all orders are half fulfilled.
Thus, many customers deliberately order twice as much (200%) as needed. Eventually, when the demand defrosts and production capacity increases, they suddenly cancel orders. This action causes serious overproduction and then production halting.
4. How to Avoid the Bullwhip Effect
- Accept its existence
The first and most important step is to accept the presence of this effect. Many companies don’t admit that they sometimes make mistakes. That makes it hard to find solutions without realizing the problems.
- Coordination in the supply chain
As mentioned above, the bullwhip effect occurs due to a lack of coordination among entities in the supply chain. It is perhaps because of the existence of conflicting goals. As a result, the information is not updated in real-time and lowers the efficiency of the distribution channel. And obviously, trying to cooperate and share will be the most optimal way.

- Optimizing supply chain entities
Reducing the number of suppliers as well as intermediaries in the supply chain can help limit the impact of the Bullwhip effect. Because the simpler a supply chain is, the easier it is to communicate between them which will reduce information magnification.
- Reduce order size
This will allow businesses to react to the market more flexibly. As consumer demand changes, businesses need to be able to adjust their inventory quickly by ordering smaller and more frequent shipments.
- Maintain a stable price
A stable price level will greatly contribute to keeping a steady demand. This will limit fluctuations in demand information between subjects. Therefore, the impact of the bullwhip effect will be minimized.
Phan Quyen
FURTHER READING
Need to reconsider the practicality when using, so is the EOQ model still relevant?













