Classification of bills of exchange
On the basis of the payment term
- At Sight Bill: after at sight bill of exchange be presented, the payer is obliged to immediately pay the amount on the draft to the beneficiary without giving any reason to delay or refuse to pay if the bill is accepted and issued in accordance with the provisions of the bill of exchange and without any reason for suspending its payment.
- Usance bill: the due date of this type will be calculated from the date of presentation for the acceptance of the drawee. Payment will be made at a specified future date.
On the basis of accompanying goods documents
- Clean Bill of Exchange: this type, the payment is made without any commercial document (goods document). It is often used to pay fines, compensation, fees such as insurance premiums, transportation fees, etc, or used to claim money buying imported by traders trustworthy.
- Documentary Bill of Exchange: This type of draft is issued to the importer (payer) accompanied by a set of cargo documents. The payer won’t receive the documents until making the payment.
On the basis of the nature of the transfer
- Nominal Bill: This bill of exchange clearly states the beneficiary’s name. It does not include a pay-to-order clause, thus, it is non-transferable.
- Nameless/Bearer Bill: This type does not include the name of the beneficiary, but the phrase “pay to the bearer”. Thus, the person holding it is entitled to the benefits of the bill.
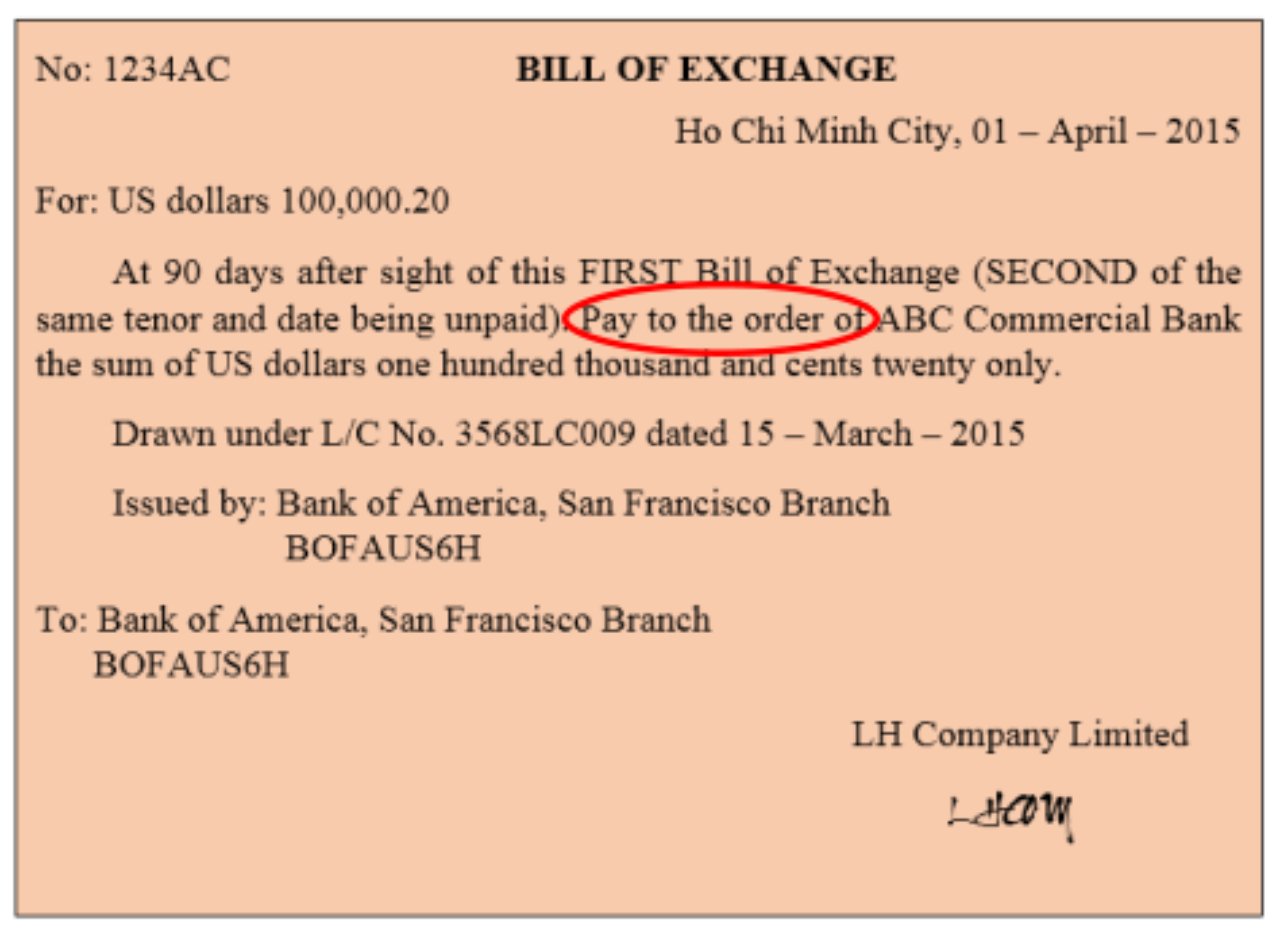
- Order Bill: The bill of exchange is paid to the order of the beneficiary. This type can be transferred by signing on the back of the bill (referred as an endorsement). The phrase: “Pay to the order of…” is often seen.
On the basis of the subject of the bill of exchange
- Trade Bill: issued by the exporter to claim money from the importer or L/C issuing bank.
- Bank Bill: issued by the signing bank, ordering its agent bank (or branch bank) to pay the amount stated on the draft to the beneficiary.
On the basis of the acceptance status:
- Non-accepted bill of exchange: this is a bill of exchange that has not been accepted, thus, the drawee is not bound to pay the bill. However, refusing to pay or sign the acceptance can make the drawee be sued out of court.
- Accepted bill of exchange: after signing for acceptance, the drawee is immediately obligated to pay the bill of exchange at maturity.

Activities related to bills of exchange
Acceptance
Acceptance is the drawee’s commitment to unconditionally pay when the bill is due. The payer (bank or importer) must write: “Accepted to pay on … (date)” and sign on it.
Endorsement
Endorsement is commonly used in transferring a bill of exchange from one beneficiary to another. The beneficiary has to sign on the back of the bill (called endorsement), and then transfers it to the next beneficiary (the assignee).

There are the following primary types of endorsement:
- Blank endorsement: is the type that does not appoint the next beneficiary. With this type of endorsement, the transfer is done only by hand, thus, the bill bearer will be benefited. The endorser only signs the back of the bill of exchange, or may add a generic phrase such as “Pay for …”.
- Order endorsement: The endorser writes the sentence: “Pay to the order of Mr…” and signs on the bill. Thus, the beneficiary is not specific.
- Restrictive endorsement: An endorsement that specifically appoints the name of the next beneficiary and only that person. For example “Pay to Mr … only”. This type of bill can not be transfered.
- Endorsement without recourse: An endorsement after which the next beneficiary is not allowed to ask for payment from the endorser when the payer (the debtor) refuses to pay.
Aval
An aval is a guarantee by a third party (the avaliseur) to pay the beneficiary when the bill of exchange is due and the drawee is unable to pay. The avaliseur is neither the payer nor the drawer of the bill of exchange, but usually a reliable bank.

The form of guarantee is made by writing the word “aval” on the front or back of the bill with the signature.
Protest for non payment
When a bill of exchange is refused to be paid, the beneficiary has the right to protest to the drawee. The beneficiary must file an appeal within the time allowed by law (usually within 2 working days of the bill’s due date).
Bill of exchange discounting
Bill of exchange discounting is the way banks lend business by acquiring the bill before its maturity to help businesses soon have cash. This value of money is always less than the actual value of the draft because of the discounting interest.
In general, bills of exchange are commonly used in international payments. In addition, a bill of exchange can be used as an instrument of credit when it is discounted at a bank, or transferred. Moreover, bills of exchange can be transacted in the money market.
Minh Ngo













