What is M&A?
M&A, also known as Mergers and Acquisitions, is one of the important strategic restructuring plans of enterprises. In Vietnam, the definition of M&A is defined in Article 29 of the Competition Law (2018) includes 3 main activities including merger, consolidation and acquisition. In short, M&A includes activities to gain control of a business through the form of merger, consolidation, or acquisition between two or more businesses.
According to data from financial services platform Dealogic, United Kingdom, in 2021 alone, global M&A value has increased by 63% to $5,630 billion, marking the first time surpassing the $5 trillion threshold. The total value of M&A deals in each region has increased at an amazing rate (the US has nearly doubled, Europe has increased by 47%, the Asia-Pacific region has increased by 37%).
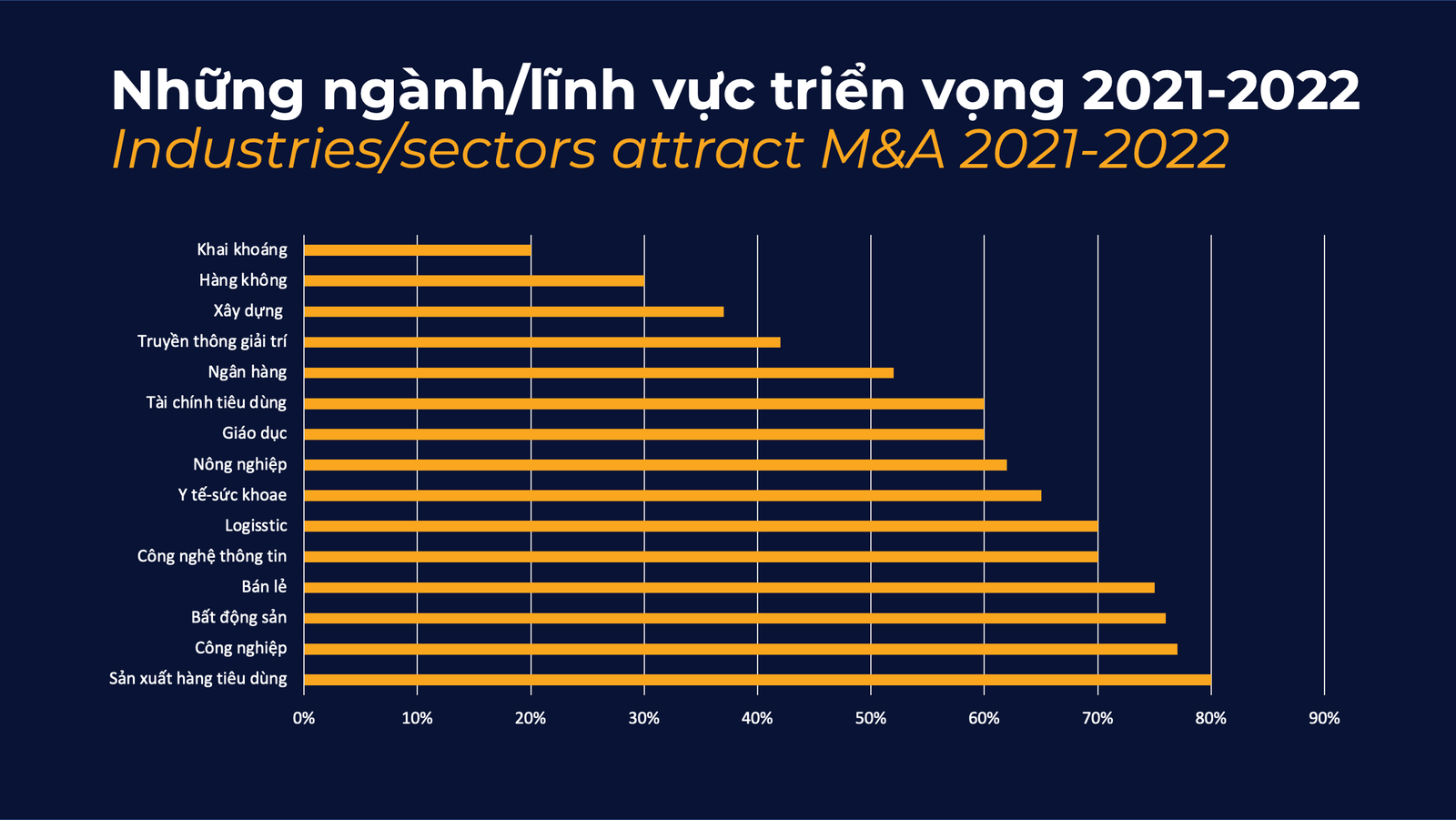
In Vietnam, according to statistics of the Vietnam M&A Forum 2021, the size of Vietnam’s M&A market has reached 8.8 billion USD in the first 10 months of 2021, with an increase of 18% compared to 2020. Particularly, with an assessment of a high growth rate of about 14-16%/year, logistics and supply chain are still forecasted to be one of the remarkable areas for M&A activities in the coming years.
What is behind M&A investment trend in logistics?
M&A is an important momentum to enhance competitiveness and open up many attractive development opportunities. Behind every M&A deal are deep business strategies and motivations ranging from geographic expansion, acquisition of new technology, etc. Here are a few typical examples:
Geographic expansion
M&A can be an effective way to expand a company’s geographic reach. For example, Regency Transportation & Distribution, a trucking company in Massachusetts, acquired S&M Transport in New Jersey in April 2020 to expand its operations in this area. Buying a new locally established company can be much more economical and easier to compete for market share in a new market than trying a gradual expansion.
Technology
Gaining new technology is also a strong motive for M&A decisions. One of the reasons Omnitracs, a digital transformation business in transportation, acquired VisTracks is to own VisTracks mobile and cloud-enabled solutions to complement the company’s Omnitracs One Platform.
Speed
Growing a company from the ground in a new market often takes a long time, and confronting existing competitors for market share can emerge a lot of pressure. M&A will help the company quickly gain competitive strength thanks to the available resources from the old company. Ruby Has, a New York-based e-commerce business, acquired EasyPost Fulfillment (California) in March 2020 with the aim to quickly capture the market and give customers an impression of their services.
Diversify new services
Enterprises that want to supplement services they have not owned, or strengthen the quality of logistics services, can M&A with companies specialized in providing those additional products and services, in order to increase service quality and meet customers’ needs. For example, Indo Tran, a forwarding and transportation enterprise, has acquired a logistics company, Sotrans, to create a comprehensive service provider in areas where the two sides are the best at.
Broader or deeper market reach
In 2018, CJ Logistics Group decided to buy back 50.9% of the capital of two shipping subsidiaries of Gemadept Co., Ltd. Through this M&A deal, CJ Logistics has improved its customer service capacity in the Vietnamese market. In contrast, Gemandept also utilizes CJ Logistics’ resources to reach important customers such as Samsung, Orion, PepsiCo, etc.

However, M&A activities still have some limitations and threats. Many cases of ‘hostile’ M&A will reduce the competition in the market, when it destroys local or weaker businesses. Besides, the trend of M&A can also lead to employment problems such as causing many workers to lose their inherent job positions when the new owners want to restructure the workforce in the new business after M&A.
Ngoc Mai













