What is EDI?
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is a method of exchanging business information and documents between business partners, businesses. These documents can be anything from delivery notes, invoices, purchase orders, receipts, and more.
EDI is considered the first form of e-commerce used in businesses. Currently, EDI is still the most important transaction in B2B e-commerce. EDI eliminates human error, cuts costs, and reduces manual processes while effectively communicating with respective parties. All data can be sent via a mailbox allowing the other trading partner to download or view the document. When EDI documents are processed electronically, a standard format is used for computers to read and understand the transferred documents.
EDI in logistics and supply chain
EDI in supply chain management is used to arrange the transfer of many types of documents such as bills of lading (B/L – Bill of Lading), customs documents, shipping status, routing instructions, invoices, and many other related documents. Transactions are also automated and organized to facilitate the creation and transmission of invoices and other necessary data. This system replaces the existing manual method which consumes a lot of human resources of enterprises.
Supply chain can be very difficult without EDI to serve the following tasks:
- Data collection, analysis, and planning
- Synchronize information flow between actors in the chain: suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and consumers
- Smooth connection of logistics activities: transportation, warehousing, customs clearance, etc
- Risk management thanks to flexible and timely traceability of the origin of goods, and at the same time the trust of consumers.
The benefits of EDI are specifically demonstrated in the following aspects:
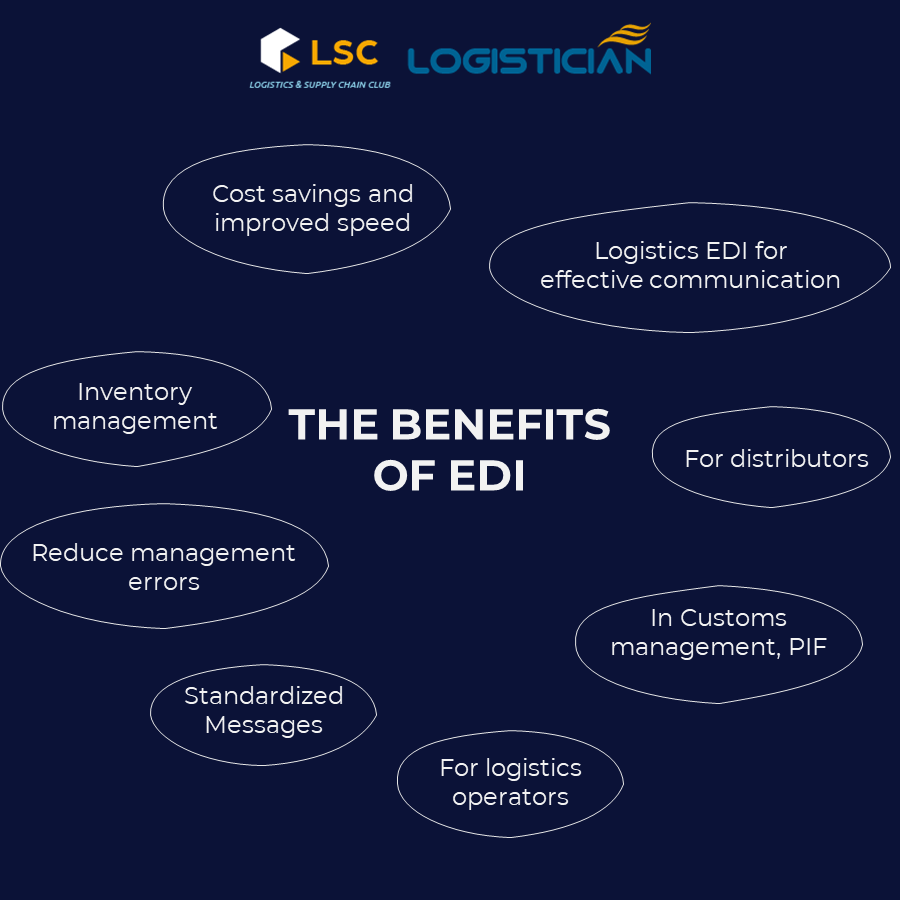
Cost savings and improved speed: EDI solutions allow the automation of internal management processes such as creation, submission and recording of any electronic transactions and interaction with the ERP system for orders. Orders, delivery notices, electronic invoices, etc., are processed without human intervention. Using the EDI system allows businesses to reduce transaction costs by 35-45%.
EDI provides real-time information that can avoid delays in the processes involved in sending and receiving products and transporting them to storage. EDI automates the entire process and allows businesses to make better use of their resources.
Inventory management: EDI helps businesses maintain ideal inventory levels for the future. EDI gives businesses access to real-time updates and the latest market trends, which they can use to streamline resource allocation and manage shortages or excess inventory.
Reduce management errors by automating the creation and delivery of commercial messages (orders, shipping notices, delivery notes, etc.)
Standardized Messages: The electronic exchange of information via EDI using a standardized language, shared by the sender and receiver. By using a common language, different information systems interact with each other, overcoming language barriers and technical barriers.
For logistics operators: EDI integrates all operations by sea, land, or air in the same communication flow and in the management of shipping ports, customs, etc.
In Customs management, PIF: EDI streamlines and provides secure administrative procedures.
For distributors: EDI helps with supply chain planning. In the case of perishable products, this management is essential because the shelf life is short and therefore the inventory must be well controlled.
Logistics EDI for effective communication: Export or import is successful when instant, secure and efficient communication is achieved between the place of origin and the final destination of the product, but also between the manufacturer and distributor, not only in terms of physical communication but also information and data, thereby promoting the perfect alignment of all links of the supply chain.
Today EDI technology is indispensable in the field of logistics and supply chains. It makes the relationship between actors in the chain more efficient. The electronic data exchange facilitates the sending and receiving of all types of documents in commercial transactions safely, quickly and fully integrated into the internal management system of the customer. customers, suppliers and any partners involved in the production whether they are commercial or administrative.
The more members of the supply chain that use EDI technology, the more controllable the entire process will be. An exporting company has to work with EDI solutions and it is very convenient for their partners to do the same as this will enhance the advantage of the system.
EDI application in retail
In Vietnam, the retail industry is facing fierce competition from many “big giants” such as BIG C, Vinmart, Aeon Mall,etc. However, supply chain cost optimization has only recently been interesting. Especially the method of exchanging documents such as Orders, Delivery Instructions, Change of orders, Invoices, Delivery, inventory information of the purchasing unit.
Big C (GO) is a large-scale retail business with the second largest market share in Vietnam. Big C has 35 hypermarkets/Supermarkets and 31 trade centers, distributing more than 100,000 items through the Big C supermarket system. With nearly 1,300 suppliers across the country, thousands of orders have been sent and delivered thousands of receipts every day. Big C has used the auto fax system in combination with the portal to support the exchange of orders and receipts with suppliers.
However, this system has not fully met the expectations of Big C’s management as well as the important requirements of the increasingly competitive retail industry in the Vietnamese market. In order to improve supply chain efficiency, better support suppliers to deal with Big C. Big C decided to apply EDI electronic data exchange technology and ERP integration solution.
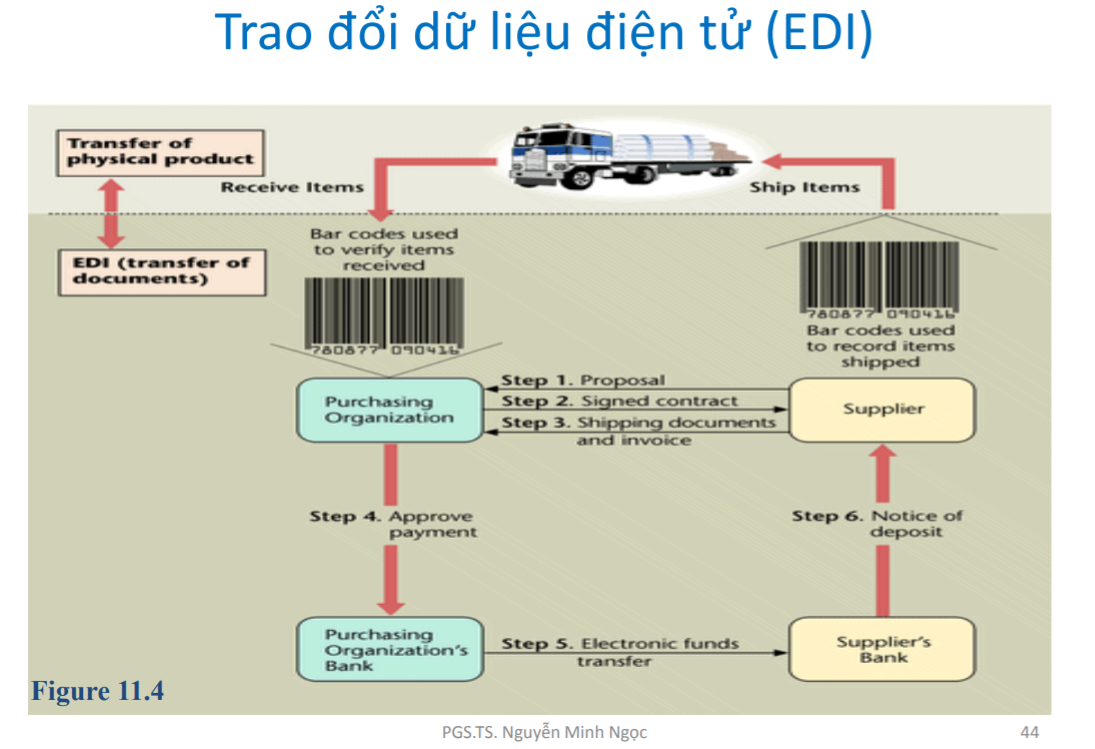
How does EDI work with Big C?
- First, supplier proposals are communicated electronically to the purchasing organization. The electronic contract will be approved on the network
- The supplier will manufacture, package the goods and attach the shipping data indicated on the label.
- The volume and price are entered into the system and transmitted to the invoicing program, the invoice will be sent to the purchasing organization.
- The manufacturer delivers the goods
- Delivery notice will be sent
- The purchasing organization receives the packages, scans the barcode of the goods and compares the data with the e-invoice received
- Acceptance of goods through electronic means
- The bank transfers money from the buyer to the supplier using an electronic money transfer method.
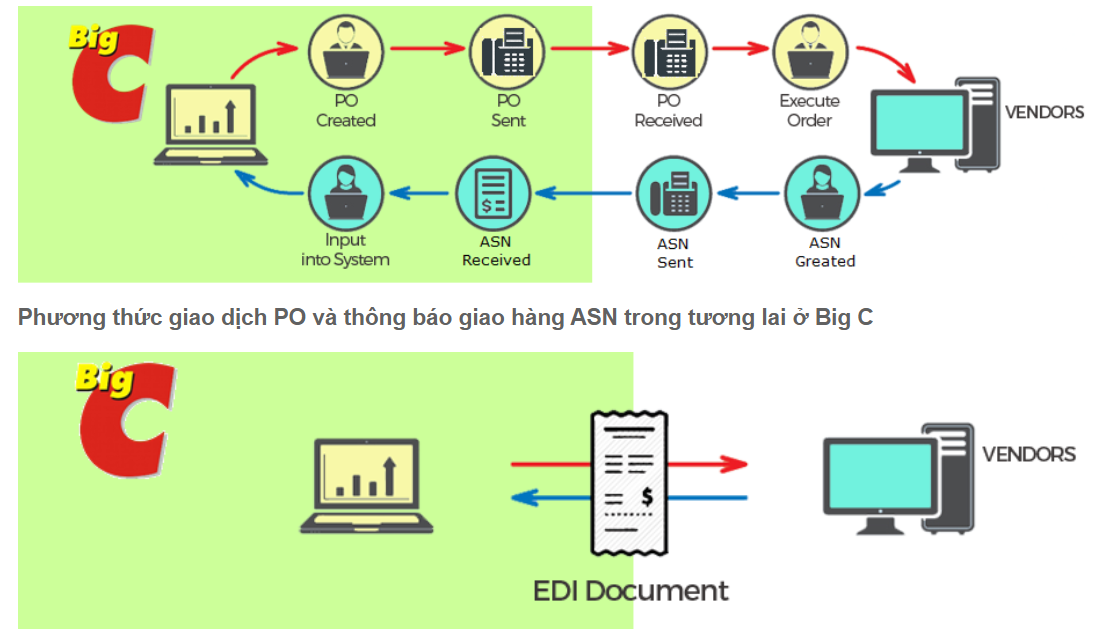
Changes to PO transaction methods and delivery notices before and after using EDI:
Hong Dao













