HIGHLIGHTS
- SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) is an alphanumeric code that is used to categorize inventory goods, including products or services.
- SKU has an important role in the management of goods and warehouses of businesses. The larger the company, the more necessary it is to use this.
- The main distinction between SKUs and UPCs is that SKUs are optimized for internal inventory control, while UPCs are standardized such that anybody (by convention) can read them.
FULL ARTICLE
What is SKU?
SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) is an alphanumeric code that is used to categorize inventory goods, including products or services.
It has parameters, properties, and unique signs to distinguish between things. It contains information such as kind of product, manufacturer, description, size, color, material, packaging, and warranty terms. As a result, this code is a critical component in inventory management.

SKU also refers to a unique location or a code segment corresponding to the storage unit. Two same products, stored in two different warehouses, will have different SKUs.
In addition, there are neither regulated nor standardized. The number of SKU codes is unlimited, each product only needs to be named according to the standards of the management unit. When businesses receive goods from suppliers, they have the choice to maintain the supplier’s SKUs or create new SKUs themselves. However, from experience, this is an internal product management code, so it is advisable to create your own SKU code. Additionally, SKUs are only relevant to available and ready-to-trade goods, nor to goods that have been ordered or are in transit.
What role does SKU play in inventory management?
SKU has an important role in the management of goods and warehouses of businesses. The larger the company, the more necessary it is to use. Some of the prominent roles include:
- Timely inventory tracking and replenishment: Using SKU allows firms to easily control product quantity. Businesses can then determine and construct an appropriate supplementary order plan (when to order and how much to order). This helps the company’s responsiveness.

- Sales forecasting: Through information about customer needs, businesses can forecast their business sales in the future.
- Shopping experience and store interface: The SKU system allows enterprises to categorize products in a variety of ways, such as item type, collection, supplier, and so on. Product management will become much more difficult, even confusion, errors will occur without this code. In response to customer requests, losing track of product location will leave a very bad image for customers.

- Means of improving service and payment: Scanning the SKU code through the payment system makes the payment process fast and accurate. After each payment, the remaining inventory will also be updated, saving inventory time.
SKU Configuration
There are various ways to name the SKU code depending on the item and the nature of the business. It is not difficult to set; simply use letters or numbers according to the convention for the information that you want to include in the SKU code. Some examples of information that should be included in the SKU code are:
- Name of the manufacturer (or brand name).
- Product Information: Material description (cotton, khaki, silk, brocade, etc.); product shape (long, short, square, round, triangle, etc.).
- Date of purchase: Include how many days, months, and years there are in a year (only the last 2 numbers should be used).
- Warehouse: If you have many warehouses, you can have a different symbol for each one based on the location of Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, etc., or by County, District.
- Size of the product.
- Color of the product.
- Condition of the item: new or used.
Combining all of the above allows you to simply set product SKUs based on category.
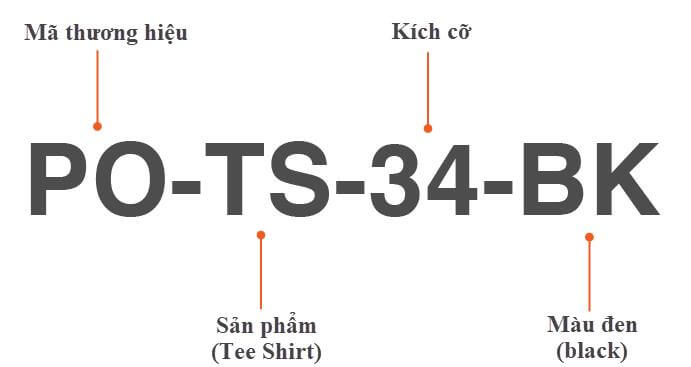
As mentioned before, setting the SKU code is completely dependent on the business nature of the enterprise. Some notes on generating SKUs, including:
- Arrange the fields in the SKU code properly: Follow the rule from broad to specific (from the category, product type to brand and finally product features). All SKU codes are applied like that instead of each code ordering a style, making it easy for employees to quickly identify the product.
- Do not use too much information: Consider what information is most important that can distinguish between products such as branch, product type, size number, color, etc.
- Easy-to-read fonts and characters: Avoid characters that seem like both letters and numbers, such as the letter “O” and the number “0.” Special characters such as “/”, “>”, “*”, etc, not only makes it difficult for staff to recall, but it can also lead to spreadsheet errors.
- Use warehouse management software with SKU such as ASOFT-WM, SAPO, Kiotviet, etc. Code management with traditional software such as Google Sheets or Excel can lead to shortages or excesses, uncontrollable errors.
Distinguishing SKU and UPC
UPC (Universal Product Code) is a type of barcode that is a sequence of 11 digits (with values 0 to 9) with a check digit at the end. This is a sort of barcode that is commonly used in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Europe, and other nations to track commercial items in retailers.
The main distinction between SKUs and UPCs is that SKUs are optimized for internal inventory control, while UPCs are standardized such that anybody (by convention) can read them. As a result, the same product may have multiple SKUs yet just a single UPC in different organizations.

Table comparing the difference between SKU and UPC
| SKU | UPC |
| Depending on the management unit, usually from 8 – 12 characters. Includes both letters and numbers. | 12 characters. Just numbers, no letters. |
| SKU is created by a distributor or the unit directly managing the product. | UPC is based on existing regulations, administered by GS1 US, the US branch of GS1 international organization (formerly known as the Uniform Code Council). |
| SKU is unique, used within the company, product management units. | UPC is commonly and consistently used for a product. |
Van Anh













